1 What’s Merge Sort Algorithm?
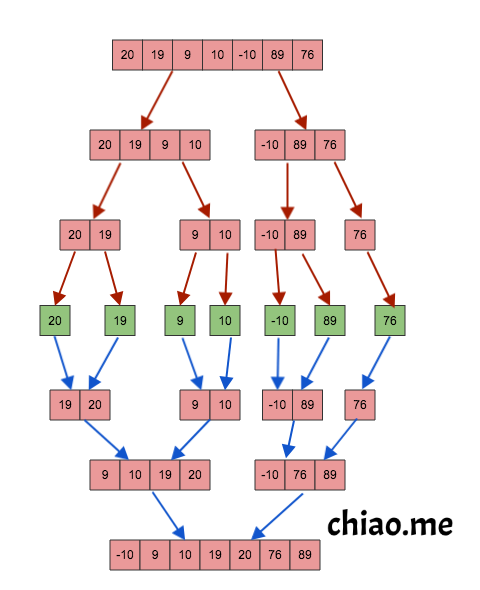
Merge sort is one of the most efficient sorting algorithms. It works on the principle of Divide and Conquer. Merge sort repeatedly break down a list into several sublists until each sublist consists of the single element and merge those sublists in the manner that results into a sorted list. Its worst-case time complexity is O(nlogn).
2 How Merge Sort works?
- Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each comprising one element that can be treated as a sorted list;
- Repeatedly merge sublists to produce newly sorted list until there is only one sorted sublist remaining
How to merge two sorted list? Firstly, the first element of both lists is compared. If sorting in ascending, the smaller element between two becomes the new element of the sorted list. This procedure is repeated until there is an empty sublist. And the nonempty sublist is appended to the new sorted list.
3 Example
4 Code Rush
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
public void mergeSort(int[] arr) {
mergeSortHelper(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public void mergeSortHelper(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if(right > left) {
int middle = (left + right) / 2;
mergeSortHelper(arr, left, middle);
mergeSortHelper(arr, middle + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, middle, right);
}
}
public void merge(int[] arr, int left, int middle, int right) {
int[] tem = new int[right - left + 1];
int i = 0;
int j = left;
int k = middle + 1;
while(j <= middle && k <= right) {
if(arr[j] <= arr[k]) {
tem[i++] = arr[j++];
}else {
tem[i++] = arr[k++];
}
}
while(j <= middle) {
tem[i++] = arr[j++];
}
while(k <= right) {
tem[i++] = arr[k++];
}
i = 0;
while(left <= right) {
arr[left++] = tem[i++];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MergeSort m = new MergeSort();
int[] arr = new int[]{10, 2, 3, 4, 9, 100, -1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
m.mergeSort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
"""
Created by Zhao Chang on 2018-08-30-01:15 in Los Angeles
Copyright (c) 2018 ACT. All rights reserved.
"""
class MergeSort:
def mergeSortFun(self, arr):
self.mergeSortHelper(arr, 0, len(arr) - 1);
def mergeSortHelper(self, arr, left, right):
if right > left:
middle = (right + left) / 2;
self.mergeSortHelper(arr, left, middle)
self.mergeSortHelper(arr, middle + 1, right)
self.merge(arr, left, middle, right)
def merge(self, arr, left, middle, right):
count = 0
i = left
j = middle + 1
tem = []
while i <= middle and j <= right:
if arr[i] <= arr[j]:
tem.append(arr[i])
i = i + 1
else:
tem.append(arr[j])
j = j + 1
if i <= middle:
tem[len(tem): len(tem)] = arr[i: middle + 1]
if j <= right:
tem[len(tem): len(tem)] = arr[j: right + 1]
arr[left: right + 1] = tem
if __name__ == "__main__":
m = MergeSort()
arr = [10, 2, 3, 4, 9, 100, -1]
print arr
m.mergeSortFun(arr)
print arr
<?php
class MergeSort {
public function mergeSortFun(&$arr) {
$this->mergeSortHelper($arr, 0, count($arr) - 1);
}
public function mergeSortHelper(&$arr, $left, $right) {
if ($right > $left) {
$middle = intval(($right + $left) / 2);
$this->mergeSortHelper($arr, $left, $middle);
$this->mergeSortHelper($arr, $middle + 1, $right);
$this->merge($arr, $left, $middle, $right);
}
}
public function merge(&$arr, $left, $middle, $right) {
$i = $left;
$j = $middle + 1;
$tem = [];
$count = 0;
while($i <= $middle && $j <= $right) {
if($arr[$i] <= $arr[$j]) {
array_push($tem, $arr[$i]);
$i++;
}else {
array_push($tem, $arr[$j]);
$j++;
}
}
while($i <= $middle) {
array_push($tem, $arr[$i]);
$i++;
}
while($j <= $right){
array_push($tem, $arr[$j]);
$j++;
}
while($left <= $right) {
$arr[$left] = $tem[$count];
$left++;
$count++;
}
}
}
$m = new MergeSort();
$arr = [10, 2, 3, 4, 9, 100, -1];
print_r($arr);
$m->mergeSortFun($arr);
print_r($arr);
function mergeSort(arr) {
mergeSortHelper(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
function mergeSortHelper(arr, left, right) {
if(left < right) {
var middle = Math.floor((right + left) / 2);
mergeSortHelper(arr, left, middle);
mergeSortHelper(arr, middle + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, middle, right);
}
}
function merge(arr, left, middle, right) {
var i = left;
var j = middle + 1;
var tem = [];
while(i <= middle && j <= right) {
if(arr[i] <= arr[j]) {
tem.push(arr[i]);
i++;
}else {
tem.push(arr[j]);
j++;
}
}
while(i <= middle) {
tem.push(arr[i]);
i++;
}
while(j <= right) {
tem.push(arr[j]);
j++;
}
var count = 0;
while(left <= right) {
arr[left] = tem[count];
left++;
count++;
}
}
var arr = [10, 2, 3, 4, 9, 100, -1];
console.log(arr);
mergeSort(arr);
console.log(arr);
5 Time & Space complexity
Time complexity:
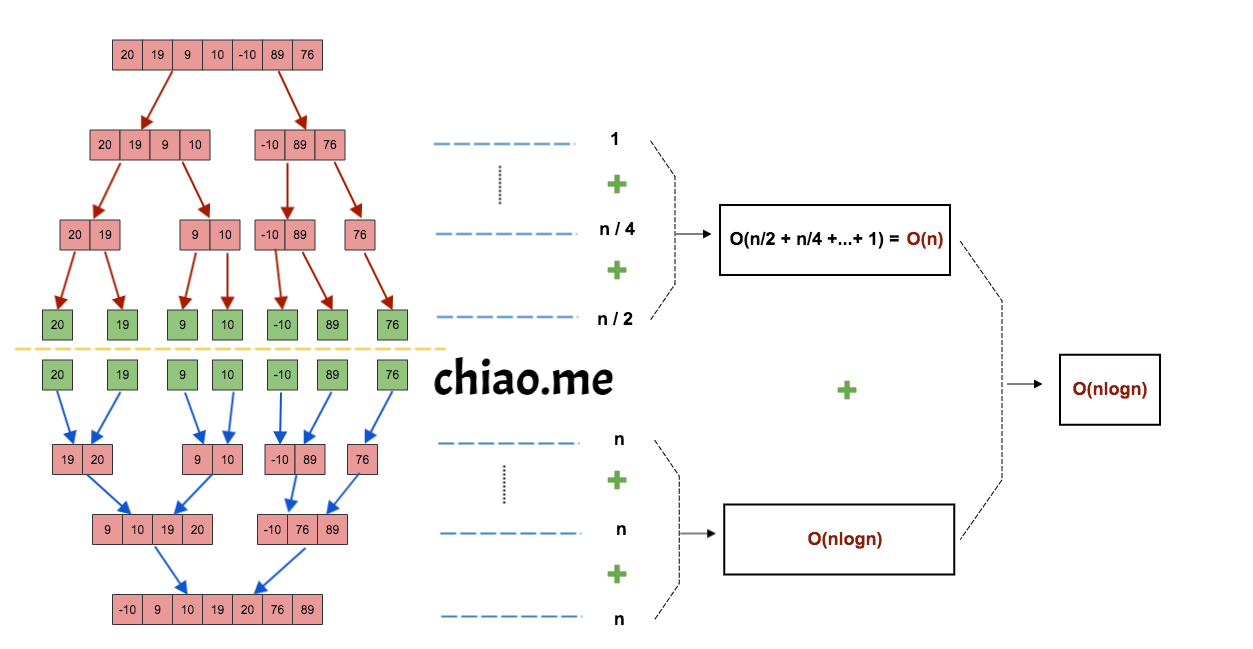
Ⅰ. Analyzing step by step:
- dividing the list into two sublists, which takes
O(1)time; - recursively sorting two sublists
- sorting two sorted sublists, which takes
O(n)time
How many times are these steps executed?
Let’s look at the tree below. Above the yellow line, each sublist for each level needs to be divided into two sublists, which takes O(1) time. For one level, it should take O(m/2) time(m is the number of the sublists for this level).
From top to bottom: Level 1: O(1), Level 2: O(n/4), Level 3: O(n/2).
So the time complexity here is O(n/2 + n/4 + ... + 1) = O(n).
Now, we analyze the tree below the yellow line. For each level, the program needs to merge sorted sublists to produce newly sorted sublists(list), which takes O(n) because of traversing every element. What’s more, there are log(n) levels. Thus, the time complexity here is O(nlogn).
Time complexity is O(nlogn + n) = O(nlogn).
II . Analysis using master theorem:
Merge Sort is a recursive algorithm and time complexity can be expressed as following recurrence relation:
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + f(n)
According to Master Theorem, the time complexity is O(nlogn)
Space complexity:
According to our code(Java), only two statements can produce extra space in mergeSort function. One is middle, which takes O(1) space complexity. The other is merge function, which takes O(n) space complexity because of the existence of a temporary array(tem). Additionally, the algorithm is a deep-first algorithm. There is only one merge function can be executed at some point. Therefore, the space complexity here is O(n).
6 Interview Skills Sharing
- How to prepare for interviews?
- How do I prepare for a software engineering job interview?
- Interview Preparation for Software Developer;
References
1.https://www.interviewbit.com/tutorial/implementation-of-merge-sort-algorithm/ 2.https://www.interviewbit.com/tutorial/merge-sort-algorithm/ 3.https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/merge_sort_algorithm.htm 4.https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/merge-sort/ 5.https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10342890/merge-sort-time-and-space-complexity 6.https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/297160/why-is-mergesort-olog-n